As stated before, the first person singular form of a regular verb form or to-be verb form is often the same as the simplest form of the verb. However, that's not always true with irregular verbs and words in the to-be form, such as was or were. Look below to continue learning about the other subject forms and examples of their verb conjugation English use. Spanish verbs can undergo a stem change for different "persons," can change in spelling only in the yo form, or can change almost completely in every different form.
Below are a few categorical ways verbs can change, along with a few examples. An exhaustive list of all irregular verbs would be much too long, but this will prepare you for some of the types of diversity you will see. You'll notice that the majority of irregular verbs end in -er – in fact, about 72% of -er verbs are irregular. It may not be the most enjoyable part of learning a language, but putting in some time to memorize these verb conjugations will make your life much easier. Yo corronosotros corremostú corresvosotros corréisél/ella/ud.
CorrenIrregular verbs can have stem changes that make it difficult to tell which verb is concealed underneath, just like the surprising variety of inflected English forms of "to be" (am/are/is). Consequently, the conjugations for irregular verbs deserve some extra attention and, in the end, just need to be memorized. Whereas nouns are at the center of the English language, verbs are at the heart of Spanish. Native speakers play with verbs in tense, conjugation and verb choice to ever so slightly change the meaning of sentences. Worked into verb conjugations are not only time markers but also grades of politeness and emotion toward a particular event.
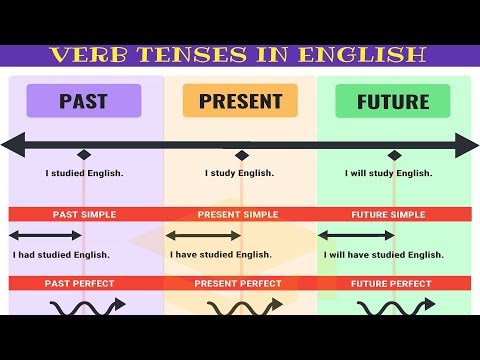
You already know quite a lot about how to get verb forms to agree with the subject in a sentence. If you're learning English as a second language, you may wonder about imperfect verb conjugation. In addition to the six different person categories, there are also twelve different tenses that each call for a different conjugation of verbs based on when an action or state of being is occurring.
Look at each tense and note how the suffixes change a regular verb form during standard conjugation. For this example, we'll use first person singular form, I. The plural vosotros is always the same as the infinitive, but with a final -d instead of an -r in the formal, written form; the informal spoken form is the same as the infinitive. The singular vos drops the -r of the infinitive, requiring a written accent to indicate the stress.
Note that other words that end in y will have different endings, such as pray becoming prayed, or lay becoming laid. That's because many irregular forms have their own unique verb conjugation patterns. These are irregular verbs which have different English verb conjugations, such as these examples. Conjugation gives your reader or your listener important background information.
In the examples above, you saw how to use words to describe the number of people or things someone's talking about in verb conjugation English subject placement. You also saw examples of how you can tell when an action will occur in verb conjugation English tenses. Additionally, verb conjugation also explains how much of an action has taken place, the gender of the people that receive an action, and the mood of an overall sentence.
As you can see, among all the subject matches with all the regular verb conjugations the only change occurs with the third person singular form. This is the standard pattern with regular verb forms like to work, making this English verb conjugation easy to remember. During verb conjugations it will change from the infinitive form depending on the grammatical subject. This means that you add different suffixes to the infinitive form depending on who you're referring to in a sentence. Hola Anil, you've asked a really nuanced question, which is great, but difficult to answer in this form.
In general, "would have" and "could have" can be translated into a number of tenses and moods in Spanish depending on the context. Sometimes we need the subjunctive, sometimes we need the future tense, sometimes we need the conditional mood and sometimes we need another compound tense. In fact, our level 3 course, El Conversador, has 12 weeks of curriculum almost entirely dedicated to this question. Try to focus on the examples I have provided in the article and other important tenses such as the present tense, past tenses and the hack for the future "ir + a". As the Spanish future tense is formed in exactly the same way as the Spanish conditional tense, these 12 irregular verbsapply equally to both tenses.
The sentence "I was dancing" would be replaced with "I danced" in Spanish. For many English speakers, learning all the conjugations of Spanish can be difficult enough. Once you get into choosing between the two versions of "to be", you feel like you could almost give up. As soon as your "ah-ha" moment arrives, you'll just have to worry about putting it into practice.
Even people who have been studying Spanish or living in a Spanish-speaking country for a long time can get mixed up and make these mistakes. The future has two main forms in Spanish, the imperfect future and the simple one. The compound future is done with the conjugated ir (which means "to go," but may also mean "will" in this case) plus the infinitive and, sometimes, with a present progressive verb added as well.
The indicative mood has five simple tenses, each of which has a corresponding perfect form. In older classifications, the conditional tenses were considered part of an independent conditional mood, but now are grouped with the indicative. Continuous forms are usually not considered part of the verbal paradigm, though they often appear in books addressed to English speakers who are learning Spanish. Modern grammatical studies count only the simple forms as tenses, and the other forms as products of tenses and aspects. Again, this action word is the same as the root of the infinitive form that we will change during the conjugation of verbs in other tenses. This will be highlighted later in the guide to reflect tense change in English verb conjugation.
None of these verbs encode motion in their meaning, nevertheless, they turn up in directed motion sentences. As we said above, verbs change to reflect the who and the when. Some verbs, like ser and ir, are extra irregular and transform not only depending on person, but also depending on tense. You'll notice that the simple future tense includes the whole infinitive plus a pattern of endings.
The easiest type of irregular verbs in Spanish are the ones that require stem-changing but keep the regular endings. By the way, the stem of a verb is the result you get when you remove the infinitive suffix (meaning the -ar, -er, or -ir) from the infinitive form. For example, the stems of deber, hablar and vivir are "deb-", "habl-" and "viv-". As stated above, deciding whether to use the preterite or the imperfect can present some difficulty for English speakers. But there are certain topics, words, and key phrases that can help one decide if the verb should be conjugated in the preterite or the imperfect.
These expressions co-occur significantly more often with one or the other of the two tenses, corresponding to a completed action or a repetitive action or a continuous action or state in the past. The -g- is present in the present subjunctive of such verbs. These verbs are often irregular in other forms as well.
Another bonus, there are only a small number of irregular verbs. Generally, you need context with these forms just as you do in romance languages, but not always, which is how they are often overlooked as a potential imperfect verb conjugation in English. Learning verb conjugation expands your speaking ability by letting you describe yourself and others in new ways. In this lesson, you'll learn how to use the conjugation of verbs to express yourself and others and their actions or state of being. You'll also discover how to tell in speech and writing when an action takes place and understand how to express yourself in different situations. Notice that the infinitive stem is present in the nosotros and vosotros forms of these verbs.
What Does Verb To Be Mean In Spanish This is common to irregular verbs, but not always the case. After taking a few minutes to look at Spanish verbs, you will find that beneath the surface they are full of surprises. Verbs which do not follow the dominant conjugation scheme are called irregular verbs, and they are extremely common in Spanish . This guide will help prepare you to encounter these tricksters in the wild and understand their irregular ways.
Every language has its rules and Spanish makes no exception . There's nothing scary about a little grammar once in a while. The same as in English, the Spanish language has regular verbs that follow certain rules and irregular verbs that usually go wild and need to be learned by heart.
Today, we are studying a few eloquent examples from both sides. In Spanish grammar, continuous tenses are not formally recognized as in English. However, one can also say sigo leyendo ("I am still reading"), voy leyendo ("I am slowly but surely reading"), ando leyendo ("I am going around reading"), and others.
The imperative mood has three specific forms, corresponding to the pronouns tú, vos, and vosotros (tú and vos are used in different regional dialects; vosotros only in Spain). These forms are used only in positive expressions, not negative ones. The subjunctive supplements the imperative in all other cases (negative expressions and the conjugations corresponding to the pronouns nosotros, él/ella, usted, ellos/ellas, and ustedes). The main verb expresses the meaning and content of the action. In simple tenses the main verb appears alone, while in compound tenses it appears together with an auxiliary.
When it is alone, the main verb is conjugated; when it is together with an auxiliary the main verb takes the participle form. Personal forms are the conjugated forms of a verb in one of the Spanish tenses . When conjugated, the verb agrees in person and number with the subject of the sentence, which is why we typically omit subject pronouns in Spanish. The Spanish conditional tense is easy to conjugate and has relatively few irregular verbs. Your challenge is to remember when and where to use it correctly.
In addition to the convenience of the conjugations, the conditional tense in Spanish is used in a similar way to how we would express conditional ideas in English. Every time you think you could use a word like 'would', 'could' or 'should' in English, it is likely there is a Spanish equivalent. Finally, you have third person singular and third person plural in typical verb conjugation English use. For example, you may hear you all or you guys or even youse .
In writing, however, for both singular and plural forms, you use the word you in verb conjugations. You use this form to speak about yourself and someone else in verb conjugation English use to describe you and another person performing the same action in a sentence. In this case, instead of using the pronoun I, you use we. The essence of verb conjugations are to match the subject with the appropriate verb based on the time period.
There are multiple verb conjugations, and each expresses different time periods and are used differently based on context. Which one you use depends on the message you want to share. The directional construction would then determine the overall shape and meaning of this type of sentence. Changes in only the first-person singular form of a verb are very common. Hacer and estar are examples of a verb for which the only irregularity is in the yo form.
Escoger is an example of a verb that follows a rule for changes in the yo form. The reflexive use of se is the first one learned by most students of Spanish. In English, reflexive constructions are generally formed by using words like "myself", "herself", "themselves", etc. along with the verb. In Spanish, reflexive constructions are formed by using a reflexive pronoun with the verb. Se is a pronombre átono, and follows the same rules as other pronombres átonos as far as its position with verbs. What sets se apart is that it has multiple meanings in Spanish.
It's also important to note that in some cases, as with reflexive verbs, se is only the form for the 3rd person and Ud. Forms; the first person and tú pronouns in those cases are me, nos, te, and os. The 16 "regular" forms include 8 simple tenses and 8 compound tenses. The compound tenses are formed with the auxiliary verb haber plus the past participle. Verbs can be used in other forms, such as the present progressive, but in grammar treatises they are not usually considered a part of the paradigm but rather periphrastic verbal constructions. When learning a new language, it's easy to feel overwhelmed by the grammar rules, unfamiliar pronunciation and all the new words.
In order to not lose your motivation, it's a good idea to concentrate on the most common words at the beginning, such as the most common Spanish verbs. You'll come across them everywhere, memorize them quickly and be able to use them right off the bat. The preterite tense is utilized frequently as it is used to describe actions that have been started and completed in the past. For some Spanish learners, the preterite tense can be one of the most difficult to learn because there are several irregular verbs that you have to memorize. Many Spanish verbs are completely regular, meaning that they follow a specific pattern of conjugation.
In this lesson you will learn to conjugate regular -ar, -er, and -ir verbs . Before you can do that, you must memorize the following subject pronouns. 'Tuviera' is actually the imperfect subjunctive tense which is an advanced grammar topic. It is a topic that you should get to eventually but don't let it distract you. I put it here to show how the conditional is used correctly in Spanish conditional sentences. Typically, verb endings will be predictable based on their infinitive form.
For example, a verb ending in a consonant, such as the p in the word jump, would only need an -ed ending to change its tense. The verb smile ends in an e vowel that is silent, and so you only need to add a -d ending to change it tense. Each of these different tenses in English verb conjugation describe an action taking place at different times. In standard verb conjugation English use, present events occur right now, like in I or are ongoing. The past events occurred in the past, some of which are ongoing.
You also have the future, which explains that actions will happen in the future, many of which will continue further into the future. You complete the verb conjugation of these tenses by adding an -ed, -ing, and often a linking word. Pronouns change depending on where and how they're used in a sentence. They can change depending on whether you're expressing possession, direction, or using them after prepositional phrases.